Sport and the people who participate in it are central to the curriculum of the degree programs offered by Faculty of Physical Education and Sport. Through various modules and using a range of academic disciplines, students are able to examine and analyze the sporting performance and experience. This chapter is designed to provide students with basic terms used in sport and exercise at the very first stage of becoming a professional.
Ability is possession of qualities (especially physical qualities when speaking about the sport area) required to perform a given movement pattern. A skill is a capacity to perform it well. Skills are usually acquired or learned, as opposed to abilities, which are often thought of as innate. Talent is the potential or factual ability to perform a skill better than most people.
Physical activity is any body movement produced by skeletal muscles and resulting in energy expenditure.
Exercise is a physical activity that is planned, structured and repetitive. It involves repetitive movements of the body done to improve or maintain one or more of the components of physical fitness—cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, flexibility, and body composition
STANDING POSITION: standing position can be performed with both legs parallel to each other, feet together, with toes pointing forward; or with feet slightly apart, hip-width apart, or wider than shoulder-width apart. We can stand on one or both feet and shift our weight from foot to foot, or assume tip-toeing position. As the body is still supported on the feet, squat is also considered a form of the standing position. Depending on the flexion at knees, which can be slight or full, half squat is also described. Balancing on one foot with other leg straight and high in the air, chest is down, is called scale.
Kneeling position is taken on your knees, with the hips pushed forward and back straight, or, when sitting on the feet
Move your mouse over the sample standing positions to see images:
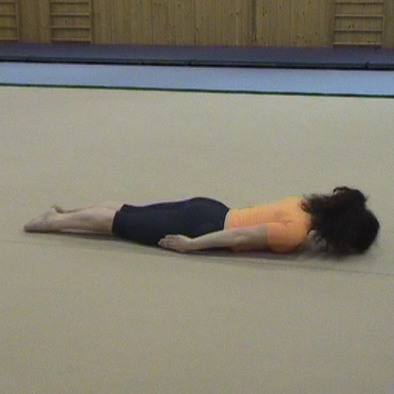
LYING POSITION: When doing exercises you can assume the lying position on your back, chest or side. These positions are also termed the back-lying, chest-lying or side-lying position. When in the back-lying position, your knees can be straight or bent, with the feet flat on the floor, apart or together. You can be also instructed to flatten/press your low back on the floor.
Move your mouse over the sample lying positions to see images:
Move your mouse over the sample support positions to see images:
SITTING POSITION: sitting position can be assumed with both legs parallel to each other, knees bent or straight, toes pointing upward, or, with the legs apart (split), or crossed and bent at the knees. Tuck position is a form of sitting position with both legs bent at the hips and at the knees, with the knees brought/pressed towards the chest. In some stretching exercises, sitting with one leg straight and the other bent at knee with the sole pressed to the knee of the straight leg, is also used.
Move your mouse over the sample sitting positions to see images:
ARM MOVEMENTS: exercises can be performed with the arms raised, stretched sideways, forward or backward, or crossed on the chest. They can be bent (slightly) at the elbows, or kept straight.
Changing the arm positions results in arm action, which is performed by e.g. circling, driving or bringing the arms forward or backward, lowering down, swinging or sweeping. The arm movements can be also done with the palms facing upward or down, or placed flat on the floor. The hands can be put, or rest, on the hips, clasped behind the head, or placed flat on the floor.
LEG MOVEMENTS: the exercise can be performed with the legs straight, stretched or bent (slightly or fully) at the knees or hips. Changing the position of legs results in leg action or footwork, which can be accomplished by raising/lowering the legs together or alternately, lunging, swinging, or driving the legs forward/backward. The leg action can be also taken with the feet flat on the floor, with the toes pointing upward, forward, inward, or outward.
UPPER BODY (TRUNK) MOVEMENTS: when doing the exercise, the upper body can be kept straight when we are instructed to stand o sit straight (tall), or (slightly) bent when leaning forward, backward, to side, or against e.g. a wall. Changing the upper body position can be also done by raising or lowering the upper body from the lying position, twisting in both directions, circling, or curling the trunk slowly and gradually.
Abdominal Curl-up
Lie on your back, with the knees bent (to about 90 degrees) and feet
flat on the floor. Avoid anchoring your feet down. Do a
“pelvic tilt”, pressing your lower back to the
floor, then slowly curl forward, lifting your shoulder blades and upper
back off the floor. Hold this “up position” for
couple of seconds, then slowly curl back down. Look toward the ceiling
(not at your knees) throughout so you don’t bend your neck
too fat forward. Make the curl-up increasingly difficult by changing
the arm positions: with arms straight, slide hands along the floor;
with arms straight, slide the hands up the thighs as far as the knees;
cross arms on the chest; bend arms and hold hands against the ears.
Thigh Stretch
While standing, bend one knee, grasp your ankle and pull your foot
gently toward your buttocks. Keep the supporting leg slightly bent and
your back straight. Use a chair for support if you need to.
Low Back Stretch
While lying on your back, grasp your hands behind one knee and bring it
toward your chest.
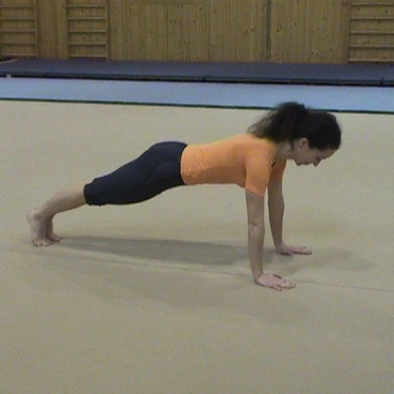
Push-up
Take the starting press-up position, position your hands at shoulder
level with your palms flat on the floor slightly more than
shoulder-width apart. Use either the knees or the feet for the pivot
point (using the feet requires more strength). Then keeping your body
in line (don’t sag!), straighten your arms to push your body
up, then lower it again until you are almost touching the floor and
repeat the whole pattern again.
In a general sense, locomotion simply means active movement or travel.
Walking is the main form of locomotion, distinguished from running. Walking is generally distinguished from running in that only one foot at a time leaves contact with the ground. During forward motion, the leg that leaves the ground swings forward from the hip. Then the leg strikes the ground with the heel and rolls through to the toe. The motion of the two legs is coordinated so that one foot or the other is always in contact with the ground.
Running is a complex, coordinated process which involves the entire body. Running is executed as a sequence of strides, which alternate between the two legs. Each leg's stride can be roughly divided into three phases: support, drive, and recovery. Support and drive occur when the foot is in contact with the ground. Recovery occurs when the foot is off the ground. The motions of the upper body are essential to maintaining balance and a forward motion for optimal running. They compensate for the motions of the lower body, keeping the body in rotational balance. A leg's recovery is matched by a forward drive of the opposite arm, and a leg's support and drive motions are balanced by backward movement of the opposite arm. The shoulders and torso are also involved.
The forward roll has a tremendous number of applications, beginning with a simple tucked forward roll, progressing through a more difficult straddle forward roll to the handstand forward roll. Handstand forward roll begins with performing the handstand. After holding the handstand position, the gymnast allows the body to lean slightly, and, while tucking the head, rolls forward and arrives in a standing position. Advanced skills may be presented such as a cartwheel, followed by handstand with transition to the forward roll.
Forward roll progression usually starts with the rock back exercise. The gymnast assumes sitting tuck, clasps the knees tightly to the chest and keeps feet together. The head is moved over the knees to form rounded back. The gymnast rocks back on to the shoulders, rocks back to the sitting tuck, and repeats the whole movement again.
The exercise can be modified by starting in the squat position, rocking back on to the shoulders and arms reaching forward to return to the squat position again. Feet are together.
Next step to take is using an inclined padded bench. The gymnast starts in the squat position, feet together, hands placed on the side of the bench; then tucks the head to the knees and pushes chin to the chest; raises the bottom and starts to roll. Arms reach forward to return to squat position.
On a padded inclined bench the teacher supports the gymnast through the roll by gently pushing the back of the head, allowing the gymnast to roll on to the top of the shoulders.
Forward roll progression may be completed by forward roll from tuck squat to tuck squat.
BASKETBALL - CHANGING DIRECTION BY CROSSOVER DRIBBLE, CHEST PASS
Crossover Dribble
The player dribbles with his right hand. Bouncing the ball in front of
his body, he passes the ball to his left hand. He continues dribbling
with his left hand and repeats the same action from the left to the
right. Through the whole movement he watches the ball only through his
peripheral vision.
Through the Legs
Crossover
The player dribbles with his right hand on the right side. The ball is
passed from his right hand through the legs to his left hand at the
moment when his right leg is in the back position. He continues
dribbling repeating the action from the left to the right. Again only
using his peripheral vision.
Behind the Back
Crossover
The player dribbles with his left hand and passes the ball from left to
right behind the body at the moment when his left leg is in the back
position. Then he continues dribbling on the right side. The same
action is repeated the right to the left when the right leg is in the
back position, again using only his peripheral vision.
One-Handed Chest
Pass
The player is standing with one leg slightly forward, weight
distributed on both feet and legs slightly bent at the knees. The ball
is held with both hands waist-high. Arms are flexed, with elbows
slightly opened to protect the ball. The pass is performed using the
whole arm. The arm extends from the elbow. The pass is completed with
the follow-through of the wrist.
Reference:
Motor Skills
Questions:
- Define the term MOTOR SKILLS and state what parts they are divided in.
- What is the basic difference between these two types of motor skills?
- Give some examples of movements referring to gross motor skills.
- At what age do children develop the skill of walking?
- What movements do fine motor skills involve?
- Why is exploring and practicing skills vitally important from the early childhood?
- Are there any other differences between the gross and fine motor skills that people may not be familiar with?
action
akce, činnost, práce
arm
action
práce paží při pohybu
leg
action
práce nohou při pohybu
activation
aktivace, zapojení
delayed muscle
activation zpožděná aktivace svalu
inhibited muscle activation
inhibovaná svalová
aktivace
alter
změnit, pozměnit
anchoring the feet
upevnění nohou (k podložce)
apart od
sebe (nohy, chodidla), rozkročmo
bend* – bent
– bent pokrčit, skrčit, ohnout,
ohýbat
bend the arm at
elbows/legs at the knees pokrčit paže v loktech/nohy v
kolenou
bend the knees/upper
body/elbows pokrčit kolena/ohnout trup-např.
předklonit,zaklonit, uklonit/pokrčit lokty
bent
pokrčení, ohnutí
bouncing
hmitání
bring* - brought
– brought přenést,
přenášet (např. paže do nějaké
pozice), pohybovat (pažemi nebo nohama)
the
arms are brought
forward paže se pohybují vpřed
calf stretch
cvik na protažení
lýtkových svalů
circle
kroužit, provádět krouživý pohyb
circling
kroužení
clasp (the hands)
sevřít, sepnout (ruce)
cross-legged zkřižmý,
zkřižmo, s nohama
zkříženýma, nohy jsou pokrčeny v kolenou
cross-legged sitting turecký
sed
curl ohnout,
svinout, postupně zavinout, odvinout (např. trup od
podložky)
curl-up varianta
cviku “sed-leh”, kdy
dochází pouze k částečnému
odvíjení trupu od podložky, trup ani hlava se
nedotknou
stehen či kolen, bez
hmitání
deteriorate
zhoršit se
drive* - drove - driven s
švihový, dynamický pohyb
vpřed (např. švihová práce nohou při
běhu), v
pohybovat
(se) švihem a dynamicky vpřed
leg
drive
záběrová fáze při běhu,
rychlý, švihový, dynamický
pohyb kolena a stehna vpřed
exercise s
cvik, cvičení,
tělesná zátěž, v cvičit,
provádět
cvičení
expenditure
výdej
fine
jemný
fine motor skills
jemná motorika
flat
plochý, umístěný plochou k
podložce
keep the feet/hands flat
on the floor nohy/ruce spočívají na
podložce
flatten
vyrovnat, přitisknout (např. bederní
páteř) k podložce při cvičení
footwork
práce nohou při styku s podložkou
grasp
uchopit, chytnout
gross
hrubý
gross motor skills
hrubá motorika
hold* - held - held
s
výdrž, v
držet
hold the position for
couple of seconds vydržet v nezměněné
pozici několik sekund
imbalance
dysbalance (svalová)
kneel
klečet. kleknout
kneeling
klek, klečení, pozice v kleku
lean* - leant or leaned s
náklon, naklonění, v
naklánět (se), klonit (se)
lean forward/backward/to
the side/against the wall nakloňte se
dopředu/zakloňte se/ukloňte se/opřete se o
stěnu
length
délka
lengthen
prodlužovat, natahovat
lie* - lay -
lain ležet
lie
on your
back/chest/side položit se na záda/břicho/bok
locomotion
lokomoce
lower
snížit, přejít do
nižšího postavení, položit
lower your arm back to
the starting position vraťte paži zpět dolů, do
výchozího postavení
lowering
pokládání,
položení, snížení
lunge
výpad, skok (prudký pohyb vpřed)
lying (position)
leh, pozice v lehu
lying on the back,
back-lying position leh na zádech
lying on the chest,
chest-lying position leh na břiše
lying on the side,
side-lying position leh na boku
motor
motorický
motor skill(s)
motorická dovednost, motorika
gross motor skills
hrubá motorika
fine motors skills
jemný motorika
movement pattern
pohybový vzorec, struktura pohybu, pohybový
stereotyp
perform
provádět, předvádět,
vykonávat, dělat
pivot s
otočný bod, střed otáčení, v
otáčet se, točit se (kolem nějakého
středového bodu, např. stojné nohy)
pivot point
středový bod otáčení
pivoting
točení (se), otáčení (kolem
otočného bodu)
point
směřovat, mířit
pull s
tah
(ve svalu), v
táhnout
push tlačit,
protlačit
push the hips forward
protlačit boky vpřed
push-up
klik, vzpor ležmo
push-up position
pozice ve vzporu ležmo
raise
zvihnout, zdvihat
leg
raise
cvik při kterém dochází ke
zdvihání nohy
raise arms
vzpažit
scale
váha (cvik na rovnováhu)
short
krátký, zkrácený
shortening
zkrácení (svalu)
sitting (position) sed,
pozice v sedu
sit-ups sedy
lehy
slide
sunout, posunovat
split sed
roznožný, čelní rozštěp
squat dřep
full squat
plný dřep
full squat, feet flat dřep
na plných chodidlech
half squat
podřep
stand s
stoj, v
postavte se, zaujměte pozici ve stoje
standing (position)
stoj, pozice ve stoji
stand with your toes
pointing forward postavte se, prsty nohou
směřují vpřed
stand/sit with your feet
(slightly) apart zaujměte stoj/sed
roznožný, postavte se/posaďte, nohy jsou (mírně)
od sebe
straddle
rozkročit se
straddle stand
stoj rozkročný
straight
rovný, narovnaný, natažený,
propnutý
keep your
knees/legs/elbows/arms straight
straighten
narovnat, natáhnout, propnout
straighten your legs
natáhněte, narovnejte nohy
strain
nadměrná zátěž,
zatížení
strength
síla
strengthen
posílit, posilovat
strengthening s
posilování, adj
posilovací (cvik)
stretch
protáhnout, natáhnout, propnout, napnout
stretch the arms
forward/backward/upward/to the sides/sideways/ předpažit/zapažit/vzpažit/upažit
stretching
protažení, natažení,
propnutí
stretching exercise
protahovací cvik
support
vzpor
back support
vzpor ležmo
front support
vzpor ležmo vzadu
sweep
máchnout, švihnout
sweeping
promáchnutí,
švihnutí
swing s
švih, švihnutí, hmit, v
švihnout, švihat, hmitat
swinging
švihání,
hmitání
tight
zkrácený, s pocitem napětí (sval)
tightness
zkrácení
tilt s
sklon, náklon, v
sklánět,
naklánět, klonit
pelvic tilt
sklon pánve
tuck (position) v
sedu pozice schylmo,
“kolébka” v leže na zádech
twist
otáčet, točit
trunk twist otáčet
trupem
weak
slabý, oslabený, ochablý
weakness
oslabení, ochablost
width
šíře, šířka
shoulder width
šíře ramen
keep your feet at the
shoulder width nohy umístěte na
šíři ramen
your legs are
shoulder-width apart nohy jsou na
šíři ramen